Case Study as part of a Web-based
Technical and Regulatory Guidance
Abandoned Bituminous
Coal Mines
Southeast Ohio
1. Site Information
1.1 Contacts
Mitchell Farley
Ohio State Department of Natural Resources
Telephone: 740-592-3748
E-mail: [email protected]
1.2 Name, Location and Description
Multiple sites in southeast Ohio (Figure 1-1) with abandoned bituminous coal
mines produce acidic conditions in surface water streams, pool water, ponds,
and lakes. The primary problems in these water sheds are remaining coal process
waste in soil and sediment contamination which then produce acidity of the
water, releasing primary contaminants of aluminum and iron.
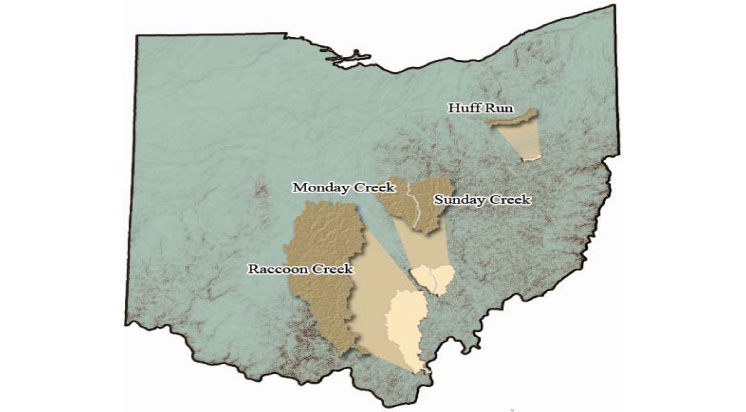
Figure 1-1. Abandoned mine drainage relative to Raccoon Creek, Monday Creek, Sunday Creek,
and Huff Run Creek in Southeast Ohio.
2. Remedial Action and Technologies
The Remedial Actions at these sites and must comply with the Clean
Water Act (CWA), the Surface Mining and Reclamation act (SMCRA), and the
Ohio Abandoned Mine Land Program. The site cleanup goal is mitigation of
ecological risk in the stream environment and is measured using contaminant
concentrations in water. Each watershed has its own cleanup levels developed
through negotiations between Ohio EPA and the primary consultant in each
watershed. Each cleanup concentration is based on the water body’s designated
use.
Since this is a description of multiple sites in four separate watershed of the expanse of southeast Ohio, multiple technologies are used:
- anoxic limestone drain—downflow wetlands or SAPS
- backfilling/subaqueous disposal—backfill toxic spoil and gob
- capping/covers/grading—cover toxic spoil and gob
- chemical precipitation—raise pH with limestone, steel slag systems
- chemical stabilization—lime stabilization of precipitants, gob, spoil
- constructed treatment wetlands—aerobic
- excavation and disposal—move and backfill gob
All have been operated at full scale for years, and there is a long-term right of entry for operation and maintenance of all treatment technologies.
3. Performance
No information reported; however, contaminant concentrations in water are
monitored to evaluate the effectiveness of each treatment technology. This
case study is reporting on multiple sites throughout southeast Ohio.
4. Costs
Cost of activities at these site are reported as a total:
- Capital: $2–3 million annually
- Operation and maintenance: ~$100,000 annually
5. Regulatory Challenges
No information available.
6. Stakeholder Challenges
No information available.
7. Other Challenges and Lessons Learned
No information available.
8. References
Go to www.watersheddata.com for
a more thorough description of the Non-Point-Source Project.
